First of all, you need to decide which years comprised the Chinese Civil War. Are you looking at 1927 to 1937, 1945 to 1949 or the entire period, 1927 to 1949?
1927-37
Who started the civil war in 1927, the CCP or the GMD?
1945 – 1949
Were the foreign powers, notably the US and USSR, responsible for the outbreak of civil war in 1945?
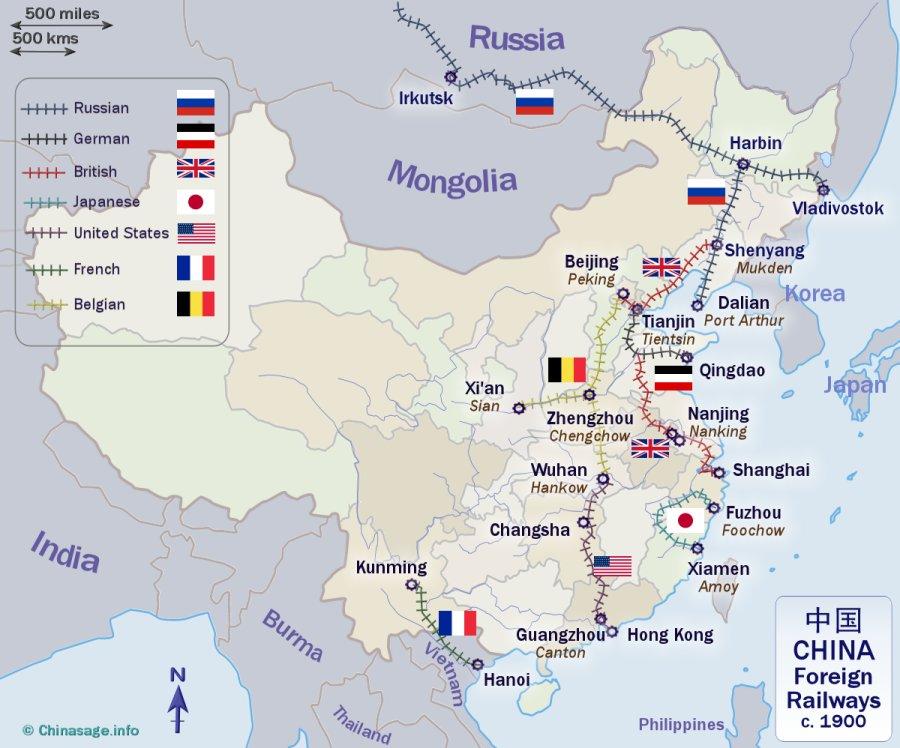
China’s Foreign Railways
Timeline
1839-42 First Opium War
1856-60 Second Opium War
1894 First Sino-Japanese War.
1899-1901 Boxer Rebellion
1911 Chinese Revolution, the Qing dynasty falls.
1912 The Guomindang was set up by Sun Yixuan (Yat-sen, creates a republic, but resigns for a stronger leader – Yuan Shikai
1915 Yuan Shikai makes himself emperor, Japan issues Twenty-One demands
1916 Yuan Shikai dies
1924 The First United Front was set up.
1925 Sun Yixuan dies and Chain Kai-Shek (Jiang Jieshi) takes over the GMD.
Long-term
The Manchu or Qing dynasty fell in 1911 leaving a power vacuum behind. The new leaders faced the same problems: the relationship with the west, the unequal treaties and ‘extraterritoriality’ resulting from the Opium Wars. One of the triggers of the revolution was the issue of foreign control of the railways. A new deal was being negotiated with Britain, the US, France, and Germany where they would control thousands of miles between them. The news of this angered many across China and led to the fall of the Manchu.
Yuan Shikai
- Former Qing dynasty general
- Improved China’s military strength after their defeat in war to Japan 1894-95.
- He became the first president of China in 1912.
- He consolidated his power rather than allow democracy, later re-establishing the post of emperor. This is the strong man argument that follows a revolution.
- Appeased Japan with Twenty-One Demands, largely due to finance.
- Growing unpopularity forced the end of his role as a monarch.
Sun Yixuan
- Chairman of the Guomindang.
- Three principles of nationalism, democracy and people’s wellbeing, set out in 1912.
- Rival of Yuan Shikai.
- Founding chairman of the Guomindang
- Helped organise the First United Front, 1922.
- Appointed Jiang Jieshi as president, who took over as chairman after Sun’s death in 1925.
Rise of the Warlords
- The fall of Yuan Shikai led to further instability in the country. Powerful warlords from the Qing Army became provincial leaders, ignoring any centralised control.
- The western countries made their own arrangements with these warlords, obtaining special privileges to secure their sphere of influence in the region.
- Some ruled fairly but others very harsh, often leading to wars between tribes or provinces.
The rule of Yuan Shikai left many revolutionaries disappointed that real change had not taken place. Intellectuals who returned from abroad criticised the country and the people who were attempting to govern it.
A. Which warlord ran Manchuria? (2:00 to 2:30) Who supported him and why? (3:00 to 3:20)
B. Which foreign countries supported the warlords? (4:00) Which two were the biggest contributors? (4:25)
C. Why did Japan and the Manchurian warlord fall out with each other? What did Japan not want to happen?(5:00)
D. How did the Europeans benefit from the warlord era? (6:00)
E. What were Sun Yixian’s plans in 1924? Why were they seen as probably failures and how were they overcome? (14:00 – 16:30)
F. Why did the Soviets support the GMD? (16:20 – 17:20)
G. Why did the GMD and CCP split? (22:00 – 24:30)
After watching the documentary, what were the main causes of the Chinese Civil War?
The Rise of Nationalism
Several events led to the increase in Chinese nationalism.
- Japan defeated China in the First Sino-Japanese War of 1894-95 and gained influence or control over Korea, Manchuria, Taiwan and the Liaodong Peninsula, as well as being forced to pay compensation.
- Chinese nationalism led to the Boxer Rebellion but this was defeated by the foreign powers, which only increased the national dislike of them.
- China helped the Allies in the First World War and expected to be rewarded for its efforts at the Paris Peace Conferences. They also expected Wilson’s Fourteen Points to be adhered to, especially ‘self-determination’. Instead, they were forced to agree to the Twenty-One Demands in 1915 and received little from the Allies (see Treaty of Versailles).
- Sun Yixian’s Three Principles, especially the self-determination for China. He set up the Guomindang (GMD) in 1912.
The Rise of Communism
Ideology of the Chinese Communist Party
Three Principles of the People
- Some Chinese people saw the humiliation of the Treaty of Versailles as a reason not to follow any western models. Communism, or Russia’s Marxism-Leninism, was seen as a viable alternative.
The Northern Expedition
This video gives a useful revision of early twentieth-century China before the Northern Expedition took place.
- Why was Chiang Kai-shek able to defeat the warlords?
- Did Chiang unify China?
The Nanjing Decade
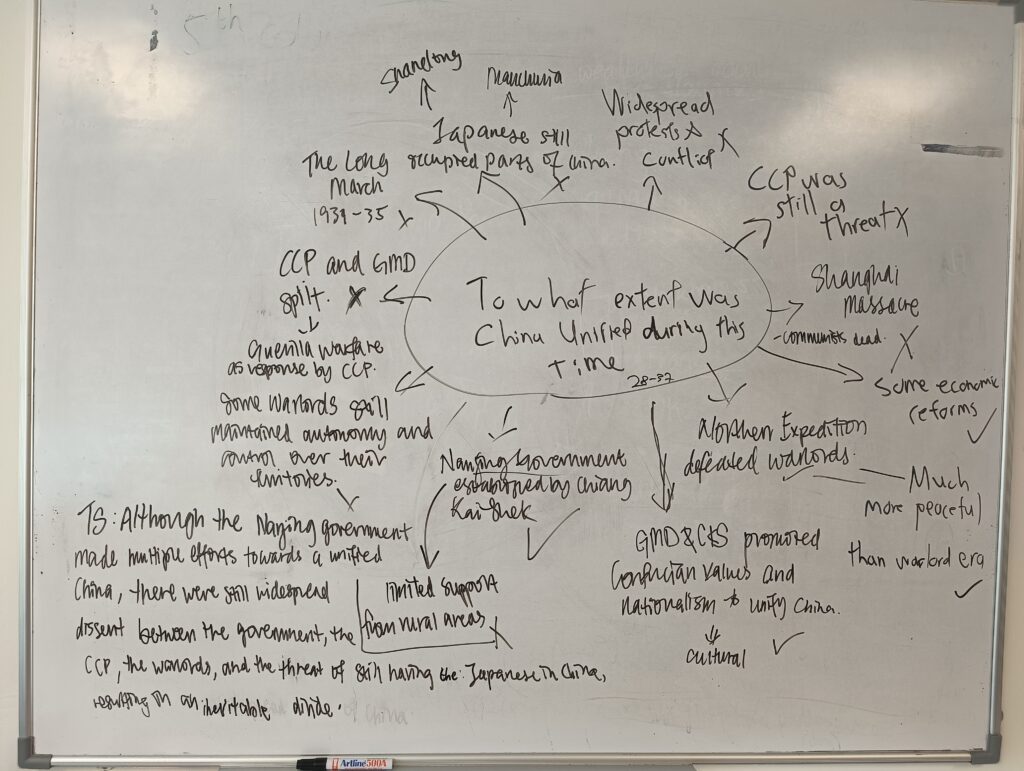
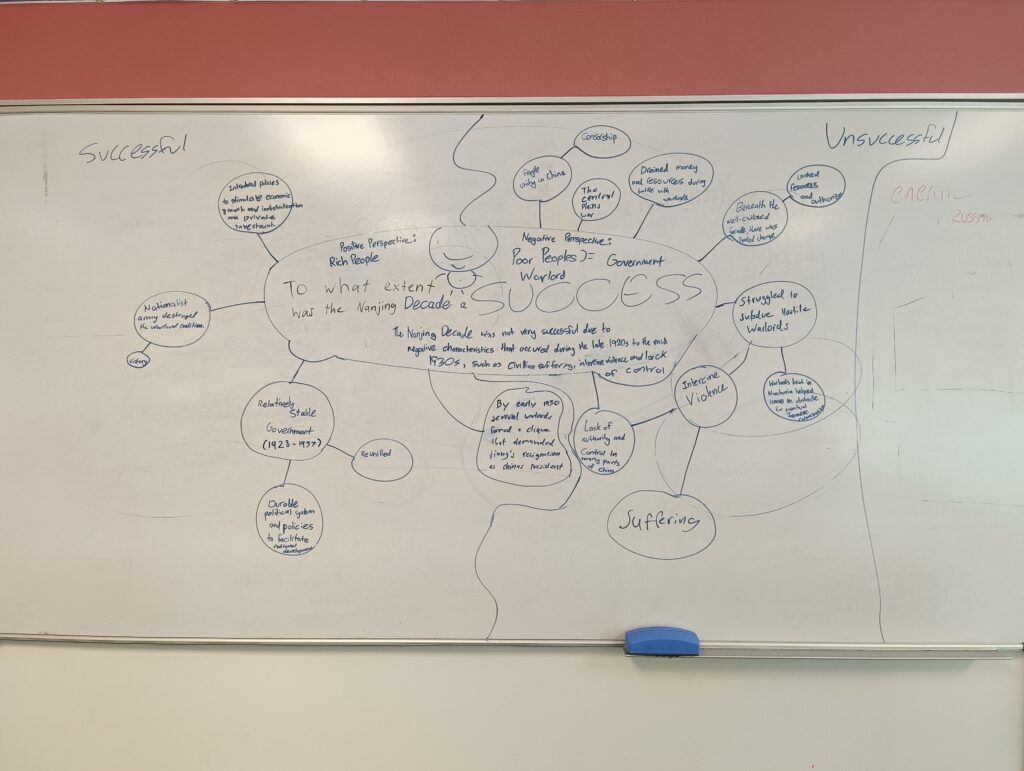
Economy
- The Chinese population grew quickly at the turn of the century but the production of resources did not keep pace.
- The Treaty of Versailles gave Japan Shandong as part of her Twenty-One Demands. Read this page to find out more.

From Causes of C20th Century Wars.
- If you are arguing that the CCW began in 1945, you can include evidence of the hyperinflation in the country during the preceding years. The more money in circulation (money supply) in an economy (the government prints more money to pay for things it needs), the higher the inflation rate.

- According to ‘Hyperinflation in China, 1937-49’, the Nationalists financed their deficits by increasing their money supply.

- When inflation is high, and continues to be so, people lose their savings and investments. This would make the GMD government unpopular and create further tensions within China.
Short-term
- The First United Front was set up to fight the warlords and unite the country. As the USSR supported the GMD, Sun Yixian agreed to the alliance with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). But after Sun died, Jiang Jieshi took over and the GMD’s northern expedition was successful, the alliance became a hindrance. Both sides had competing ideologies and Jiang decided that the CCP was no longer needed. In 1927, the GMD attacked the Communists in Wuhan, killing 15 000 or the 25 000 in the city.
- Shanghai Massacres
- The GMD continued to have internal power struggles during the ‘Nanjing Decade’. Jiang faced opposition and even coups against his leadership. As a result, the GMD’s war against the CCP was not as effective as it could have been.
Thesis Statements
- Once China was more or less united, Jiang Jieshi had no need of the alliance with the CCP. The consequent GMD actions such as the Shanghai Massacre led to two decades of internal conflict.
- The power vacuum emanating from the 1911 revolution led to the Chinese Civil War.

