- When did the British Empire begin?
- Which goods were traded?
- According to some sources, how much money was extracted from India?
- What were the positive impacts of the British Empire?
- Why is the British Empire still argued over today?
Which countries were in the British Empire?
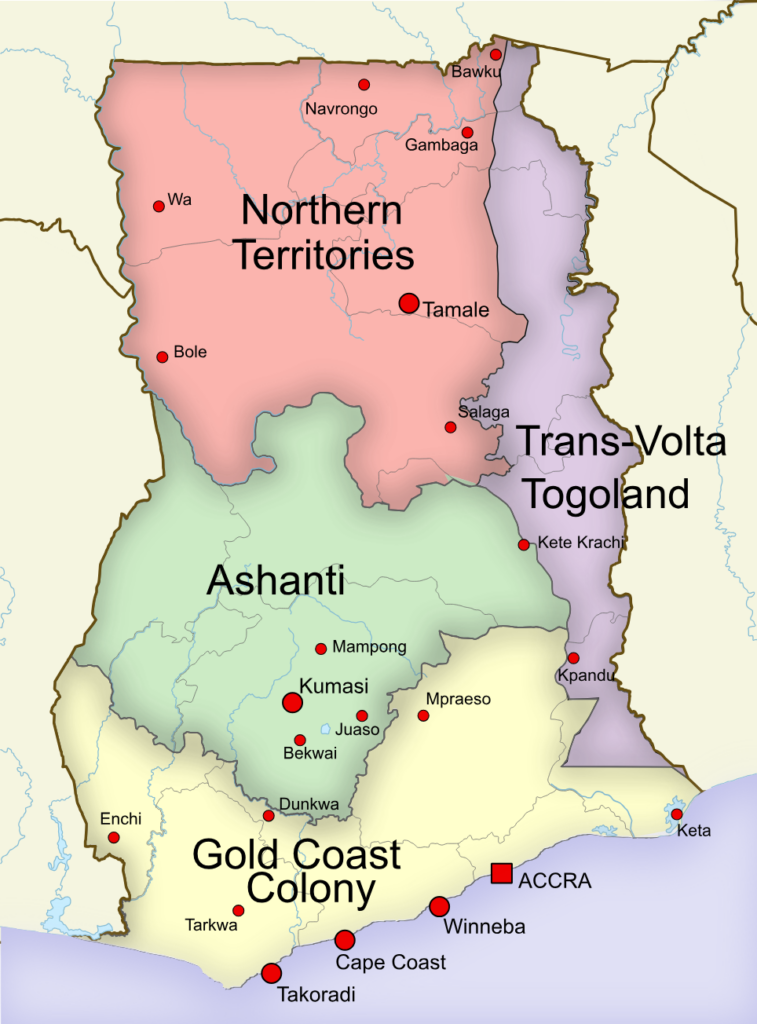
Ghana
This is a useful case study to understand how the British Empire developed and grew. Trade was the most important factor, with the ‘Gold Coast’ containing several ports, useful for both Britain and the merchants in the area. However, because of opposition, largely from the Ashanti (as they wanted power and control over the area), war followed. Britain expanded its colony in West Africa due to military success.
Ghana before Colonisation
Slavery in the Asante Empire of West Africa


Slavery

The article goes on to say that slavery was outlawed in 1874, when the British made Ghana a colony.
Military Force
Britain fought a number of wars against the Ashanti Kingdom.
British Empire – The Gold Coast
Maintaining the Empire
British Gold Coast: Early Years
British Gold Coast – Colonial Rule
Legacy of British Colonisation
The Colonisation of ‘Malaysia’
AD 700–1200: Peninsula comes under the Indian empires of Srivijaya and Cola; Borneo comes under the kingdom of Po’ni.
Many, many different people and groups have held power over lands in what is now Malaysia today. This power has changed hands because of several reasons, warfare, religion and trade being the main ones. Below are some of the key dates where the West, or Europeans, began to have influence or power of the Malay peninsula.
13th-15th centuries: Islam spread to the Malay peninsula, largely through trade.
1511: Portuguese captured Malacca
1641: The Dutch (with help from Johor) take Malacca from the Portuguese.
1796: The British began to influence the Malay peninsula
1824: Anglo-Dutch Treaty signed in which Britain took control of the Malay peninsula
Penang was annexed by the British and the Dutch colonies including Malacca were turned over to Britain in 1795 (for use in the Holland’s war against France). In 1810 Britain took control of Java and in 1819 established a base at Singapore. By 1824 the British had established control of over both India and much of Malaya.
What were the influences to Malaysia?
Legacies of the European Powers
When considering the legacies of the three European countries, these were some of your thoughts in April 2025.
A. What did the Portuguese bring to Malaysia? What mistakes did they make?
B. What did the Dutch bring to Malaysia? What mistakes did they make?
C. What did the British bring to Malaysia? What mistakes did they make? On reflection, was the British colonisation of the Malay peninsula positive or negative?

As the British influence is nearer to ‘our time’, it is usually the most scrutinised (studied).
Possible Positive Legacies of British Imperialism
When considering these ‘positives’, research and think about how much the British improved these. For example, there was education before the British arrived but did they increase and improve it?
- Acquiring Sarawak
- English language – helps trade and international relations
- Place names
- Rule of law & government
- Links to the Commonwealth
- Increase in education
- Abolish the slave trade (Raffles in Singapore)
Possible Negative Legacies of British Imperialism
One of the issues when identifying the pros and cons of this issue is whether the problem was there before British imperialism. However, you can judge if the British maintained or even worsened it.
- Ethnic division
- Economic exploitation
- Loss of culture, e.g. language
- Imported goods such as alcohol and opium (although Chinese merchants had rice wine for centuries earlier)
‘Origins of Colonialism‘ by Tirthankar Roy
Seaborne trade lead to global empires because of the actions of merchants and environmental factors.
- The powerful English (later British) Royal Navy allowed merchants and entrepreneurs to reduce their protection costs.
- A common thesis is that the Mughal Empire fell towards the end of the 18th century. Roy disagrees.
British Colonialism: A Defence
Watch from the start to 11:00 minutes.
- How do you avoid bias?
- Why does the Left attack British history so much? Why are they not impartial?
- What did the British Empire give to its colonies? Think about legacy too.

Nigel Biggar: British Empire unfairly maligned
British Colonialism: An Attack
William Dalrymple
Possible Debates: Elgin Marbles, Benin Bronzes
